2023 summary
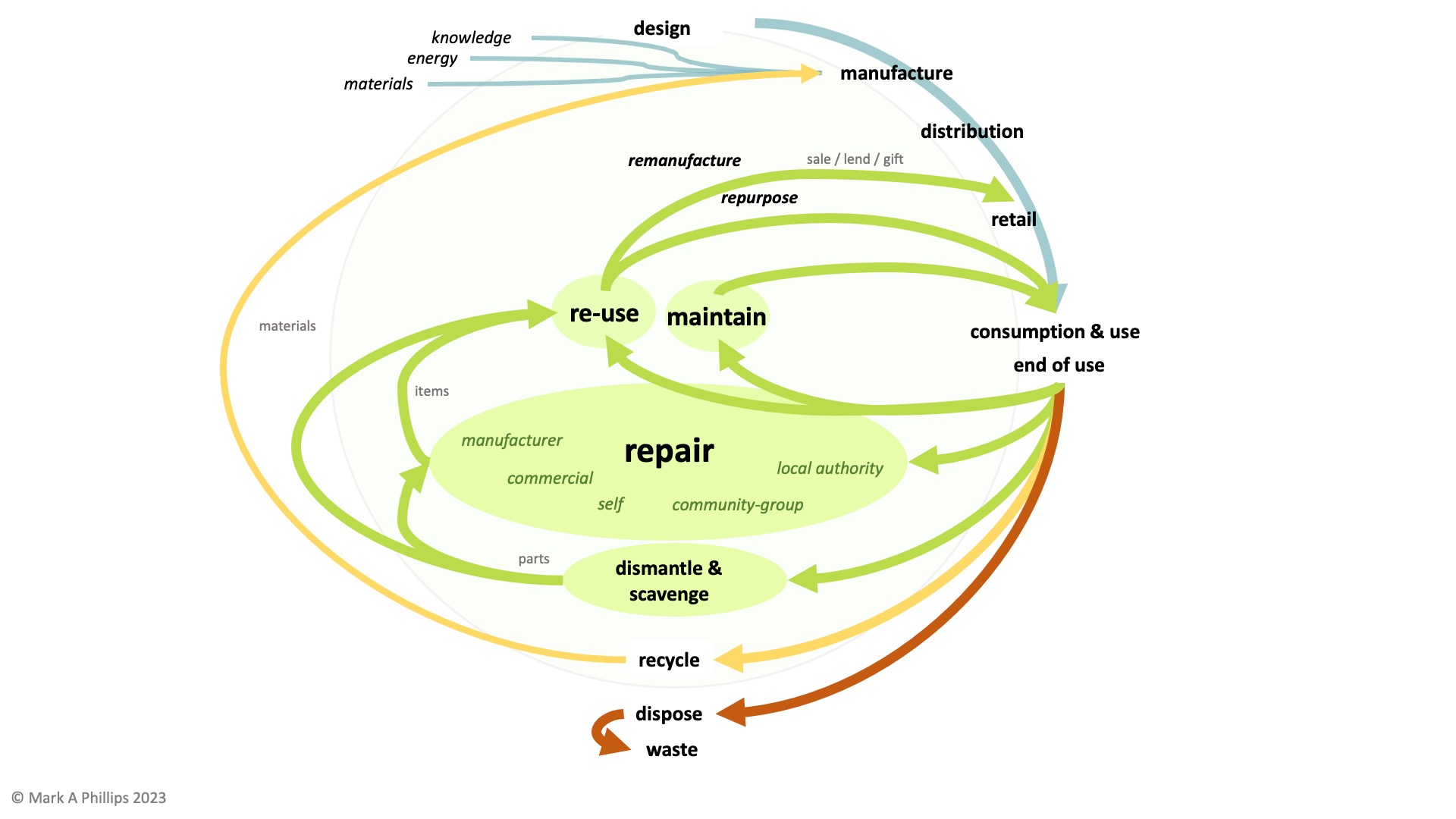
2023 has been a busy year for the right to repair movement and unbroken.solutions, here is a summary of the project and the groups I have been working with over the past few years.

January – I presented on repair at The Photographers Gallery (TPG) with the Restart Project as part of the TPG’s Small File Photo Festival
March – the project exhibited in Stirling for Circular Communities Scotland’s Share and Repair event, bringing together sharing libraries, repair and reuse communities from across Scotland.
Book and zine were published
The unbroken.solutions book and act now zine were completed, working with Struktur Design and Pure Print, and were published in June.
July– project exhibited at Sustainability Day in Hackney with Hackney Fixers.
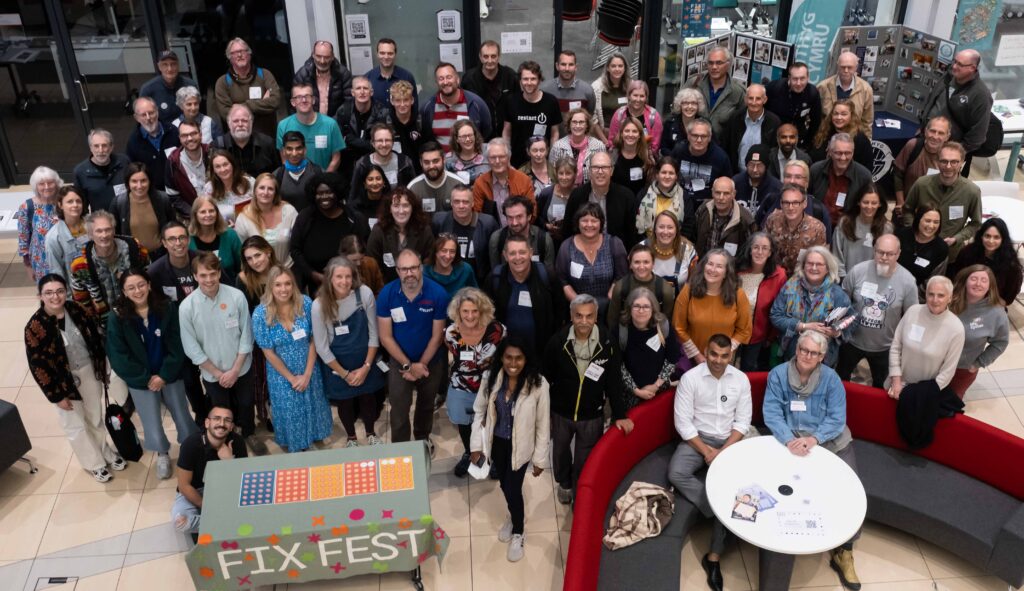
September – project exhibited and act now zines distributed to all delegates at Fixfest 2023, in Cardiff. Fixfest brought together over one hundred community repairers and activists from across the UK. It wa an opportunity to share good practice and build capability. Fixfest was also used as a platform to relaunch the Manchester Declaration as a wider and more comprehensive Repair and Reuse Declaration.

The Declaration asks UK legislators and decision-makers at all levels to support repair and reuse to thrive, by requesting the UK:
– Make repair more affordable, through tax reductions and repair vouchers.
– Expand the UK’s right to repair regulations to cover all consumer products, to strengthen design standards and remove barriers to repair for everyone.
– Introduce a repair index to help the public choose more repairable and durable products.
– Introduce requirements and targets for reuse and repair to be prioritised over recycling and provide investment to make this a reality. This should be a key part of amended extended producer responsibility rules.
– Support a new generation of repairers through repair training, accreditation and apprenticeships.
For more information and to encourage your MP to sign, see https://repairreusedeclaration.uk
Act Now Campaign
During the summer and early autumn the campaign to engage 260 UK councils, plus devolved government and UK government departments started. It asked council to provide better support for repair and reuse. The campaign sent out copies of the book, plus zine and a covering letter. Follow up emails continue to be sent to encourage more support.



The response has been a little muted (unsurprising, given the financial challenges many councils currently have) but largely positive. Some councils have actively engaged and some are including ideas in their future proposals. After some chasing, even DEFRA replied.
In October – attended BOP Bristol and Impressions Gallery, Bradford book fairs with the Photobook Club Collective.
Dead Spaces
Started research and FOI requests on empty (dead) council spaces that could be put to use to support repair and reuse. This built on the work of Sian Berry’s team in London looking at ‘Dead Spaces‘, addressing London council owned spaces that were not in use or vacant. The FOI extended that research, with a sample across the whole UK. Based on this research, it is estimated that there are around 1200 council owned properties in the UK that are empty and highly likely to be suitable for setting up sharing and repairing centres. This is an opportunity that requires little money to get started.
Visited Cambridge Repair Cafe and exhibited in Cambridge on International Repair Day.
Photographed a Right to Repair Europe (R2REurope) event at EU Parliament in Brussels, aimed at encouraging the parliament to support an improved right to repair directive. Parliament voted positively, but the Council is now in the process of watering down the proposals. Still, it is progress.
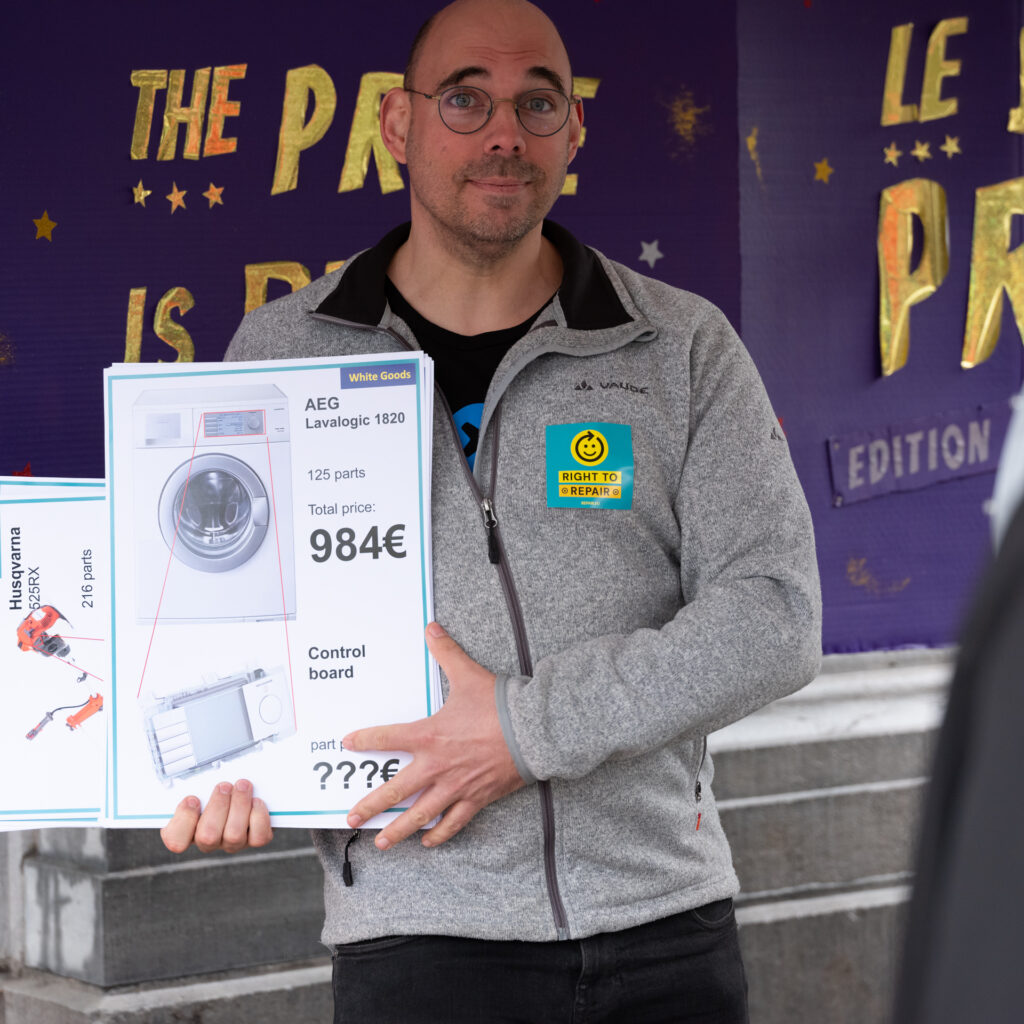




Europe has made some progress on repair in 2023 with Batteries directive: User-replaceable batteries required in all portable devices and light transportation vehicles in 2027, and Ecodesign for smartphones & tablets: Parts, tools, and documentation required for all smartphones and tablets by 2025.
In the USA in Colorado: First-ever agricultural bill supporting farmers rights to repair. In Minnesota: Broadest Right to Repair bill yet—this covers basically anything with a chip. In California: requires that electronics and appliances over $100 have parts, tools and manuals available for 7 years and in Maine: Owners & independent mechanics have access to auto telematics. Great progress for USPIRG, iFixit and the other US campaigners.
Building Capability
Also in October, visited RENEW reuse hub, run by Suez, in Manchester. Although early days, this is a major effort to re-direct goods from recycling skips, and to reuse and repair, so they last longer.
Providing facilities like this, plus share and Repair centres is going to be key to deliver any meaningful improvement in our reuse and repair capability. Sadly, the current government waste policy, strategy and proposals will do little to impact this unless there is a proper plan, rather than a the current ‘word salad’.
November– exhibited and spoke at Dead Spaces event with Sian Berry and Climate Emergency Centres in London.
December – unbroken.solutions book was added to SPP network case studies. These case studies provide examples of more sustainable photobook production. The unbroken. solutions photobook was also added to resources in Suez published “Solutions for Stuff”, a comprehensive solutions manual and guide for councils and some material was also provided to the New Zealand, Repair Café Aotearoa Handbook.
During the year regular visits were also made to community repair events and activities at Remake Newport, Penarth, Hackney, Portsmouth Share and Repair, Chesham, Stirling, Cambridge, and Renew in Manchester.
If you want to find out more about progress on repair and reuse and progress on the right to repair check out the Restart Project, R2R Europe and iFixit website and newsletters.
A busy 2023, here’s to more progress in 2024. Happy New Year!













